• Semantic AI and Ambiguity
Well known names in AI are promoting Neurosymbolics as “the next big thing”.-
One difficulty with Symbolic Logic is its effort to sweep away
ambiguity.
From an introduction to symbolic logic:
We begin with the simplest part of propositional
logic: combining simple propositions into compound propositions and determining
the truth value of the resulting compounds.
A. Propositions or statements can be thought of as the
"atoms" of propositional logic. (“Proposition” and “statement” are
often taken to be equivalent terms.)
Simple propositions are
statements which cannot be broken down without a loss in meaning.
E.g., "John and
Charles are brothers" cannot be broken down without a change in the
meaning of the statement. Note the change in meaning with "John is a
brother" and "Charles is a brother."
Wiktionary gives seven meanings for “brother”.
The first definition is: Son of the same parents as another person.
The second definition is: A male
fellow member of a religious community, church, trades union etc’
The fourth definition: A fellow black man.
The fifth definition: Somebody,
usually male, connected by a common cause, situation, or affection. The
cause can be war, and the men a band of brothers.
“brother bear” gets mentioned, as well as “brother, can you
spare a dime?”
In other words, unless you are tracking the actual meaning
of the word, almost every word (88% of them) introduces ambiguity, with the
ambiguity running up to eighty meanings, and some words boasting multiple parts
of speech (“on” as a preposition or adverb. “bar” as a noun, verb, or
preposition).
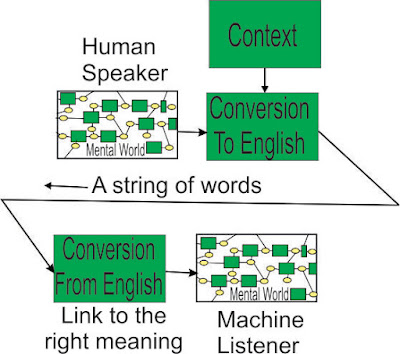
Semantic AI handles this by linking to the word and the
assumed meaning (and a few other things, like transitive and intransitive, or
another hundred different types of verb connection. Or whether a noun is
clausal – “the idea that the world is flat”). Some of these properties may not
be known immediately. Ambiguity cannot be wished away – some of it will only be
resolved by reading further or seeking other clarification, so a decision has
to be held in suspension, or in reality, many of them. A person can do this
(with a low limit on how many at once, a machine hundreds but slow).
There are other problems, the two logic states chief among them. In real applications, there is very little that is known perfectly, and some things alternate between being an input and an output - not good when your "neuro" part is a directed resistor network.


Comments
Post a Comment